Air quality in Tianjin
Air quality index (AQI) and PM2.5 air pollution in Tianjin
242.9K people follow this city

Tianjin Air Quality Map
Real-time Tianjin air pollution map
Weather
What is the current weather in Tianjin?
| Weather | Clear sky |
| Temperature | 64.4°F |
| Humidity | 63% |
| Wind | 4.5 mp/h |
| Pressure | 29.8 Hg |
live aqi city ranking
Real-time China city ranking
| # | city | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kashgar, Xinjiang | 265 |
| 2 | Baoding Shi, Hebei | 158 |
| 3 | Binzhou, Shandong | 157 |
| 4 | Daxing, Beijing | 157 |
| 5 | Fangshan, Beijing | 157 |
| 6 | Yangliuqing, Tianjin | 157 |
| 7 | Langfang, Hebei | 155 |
| 8 | Yigou, Henan | 155 |
| 9 | Dongying, Shandong | 154 |
| 10 | Shengli, Shandong | 154 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKING3D animated air pollution map
live Tianjin aqi ranking
Real-time Tianjin air quality ranking
| # | station | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Xin Lao Lu | 161 |
| 2 | Hexi Yijing Road | 158 |
| 3 | Qinjian road | 158 |
| 4 | Yuejin Lu | 158 |
| 5 | Da Zhi Gu 8th Rd | 157 |
| 6 | De wei Road | 157 |
| 7 | Xisidao | 156 |
| 8 | Dali Road | 154 |
| 9 | 4th street | 153 |
| 10 | Huaihe Road | 153 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKINGUS AQI
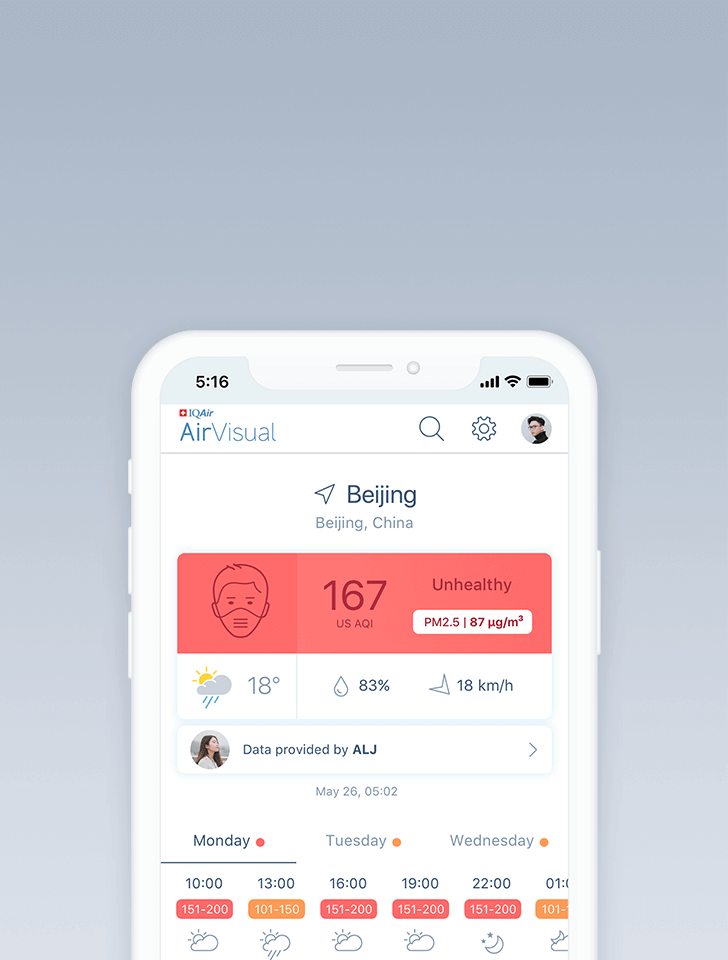
154
live AQI index
Unhealthy
Overview
What is the current air quality in Tianjin?
| Air pollution level | Air quality index | Main pollutant |
|---|---|---|
| Unhealthy | 154 US AQI | PM2.5 |
| Pollutants | Concentration | |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 61µg/m³ | |
| PM10 | 170.5µg/m³ | |
| O3 | 82.5µg/m³ | |
| NO2 | 34.5µg/m³ | |
| SO2 | 8µg/m³ | |
| CO | 650µg/m³ | |
PM2.5
x12.2
PM2.5 concentration in Tianjin is currently 12.2 times the WHO annual air quality guideline value
Health Recommendations
What is the current air quality in Tianjin?
| Avoid outdoor exercise | |
| Close your windows to avoid dirty outdoor air GET A MONITOR | |
| Wear a mask outdoors GET A MASK | |
| Run an air purifier GET AN AIR PURIFIER |
Forecast
Tianjin air quality index (AQI) forecast
| Day | Pollution level | Weather | Temperature | Wind |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monday, Apr 15 | Unhealthy for sensitive groups 107 AQI US | 73.4° 55.4° | ||
| Tuesday, Apr 16 | Moderate 69 AQI US | 78.8° 53.6° | ||
| Wednesday, Apr 17 | Unhealthy for sensitive groups 120 AQI US | 82.4° 57.2° | ||
| Today | Unhealthy 154 AQI US | 82.4° 57.2° | ||
| Friday, Apr 19 | Moderate 76 AQI US | 80.6° 62.6° | ||
| Saturday, Apr 20 | Moderate 65 AQI US | 69.8° 57.2° | ||
| Sunday, Apr 21 | Moderate 84 AQI US | 69.8° 53.6° | ||
| Monday, Apr 22 | Moderate 76 AQI US | 80.6° 55.4° | ||
| Tuesday, Apr 23 | Moderate 100 AQI US | 84.2° 60.8° | ||
| Wednesday, Apr 24 | Moderate 74 AQI US | 69.8° 59° |
Interested in hourly forecast? Get the app
AIR QUALITY ANALYSIS AND STATISTICS FOR Tianjin
What is the air quality index of Tianjin?
The city of Tianjin is located on the coast in northern China, 120 kilometres southeast of Beijing It sits on the shore of the Bohai Sea which is part of the Yellow sea. In 2016 its estimated population was over 15.5 million people. Towards the end of 2020, the air quality index recorded “Unhealthy” levels with a figure of 100 US AQI. This is based on figures recommended by the World Health Organisation (WHO). Other pollutants were recorded to be: - PM2.5 - 36 µg/m³, PM10 - 60 µg/m³, - ozone (O3) - 34 µg/m³, nitrogen dioxide (NO2) - 34 µg/m³, sulphur dioxide (SO2) - 16 µg/m³ and carbon monoxide (CO) - 1000 µg/m³. These figures are quoted as microns per cubic metre.
With figures such as these, people who are sensitive to poor quality air should wear a good quality mask when venturing outside and they should close the doors and windows to prevent the bad air entering the home. Running an air purifier would be beneficial if available, and all forms of outdoor exercise should be halted until the quality improves.
What are the main sources of Tianjin’s polluted air?
The cause of heavy air pollution in Tianjin has been discovered following the result of the combined effects of local accumulation, regional transmission and secondary transformation of pollutants.
All the heavy air pollution processes in Tianjin were tracked and analysed from 2013 to 2018. From the analysis results of 25 typical long-term heavy pollution processes, the chemical composition of PM2.5 is mainly nitrate, organic carbon and sulphate. Accounting for 40-60 per cent. It was stated that the sources of these components include both primary emission and secondary transformation. Most of the meteorological conditions are "low-altitude south-westerly winds and substantial compression of the atmospheric boundary layer". The low-altitude southwest wind was observed in the early stage of the heavy pollution process, and the height of the atmospheric boundary layer was compressed to about 200 meters. The self-purification capacity of the atmosphere was less than 20 per cent of that of clean weather, resulting in the rapid accumulation of local emissions and regional transportation of pollutants. Approximate chemical transformation effects are observed in about 50 per cent of heavy pollution processes, especially under conditions of high humidity, the contribution of secondary transformation is more significant.
It is reported that Tianjin has a relatively high proportion of road freight, and motor vehicle emissions contribute significantly to nitrogen oxides, especially diesel trucks, which account for less than 10 per cent of vehicle ownership, account for 70 per cent of total vehicle emissions. Nearly two-thirds of the transiting freight vehicles are heavy-duty diesel vehicles. At the same time, Tianjin is at an important stage of development and construction. The urban infrastructure construction and various construction projects are scattered in a wide range and high intensity.
Is air pollution in Tianjin getting worse?
It was reported in the media briefing held by the Tianjin Working Group of the National Air Pollution Prevention and Control Centre in Tianjin in the morning that the average concentration of PM2.5 in this city in 2018 was 52 16 µg/m³, the best since PM2.5 monitoring was launched. In 2018, the city's air quality improvement rate was 70 per cent, which was mainly due to the result of human effort.
Tianjin is a coastal city and faces the Bohai Sea to the east, atmospheric diffusion conditions are relatively unfavourable. The latest data shows that the average wind speed in Tianjin in 2018 was 2.19 m/s, the frequency of light winds was 35.1 per cent, the average height of the mixed layer was about 589 m, the probability of temperature inversion was 20.7 per cent, and the relative humidity was 56 per cent. These meteorological indicators are in Beijing and Tianjin. The "2+26" cities in Hebei and surrounding areas are generally in the middle reaches. Tianjin City is 50 kilometres away from the Bohai Sea. Under static and stable weather, the influence of local circulation such as sea and land breezes is more obvious, affected by the diffusion of pollutants to distant places will be inhibited, and the concentration of pollutants is affected by the local circulation It accumulates cyclically in the space. It was also suggested that in some heavy pollution processes, there are obvious convergence flow fields in and around Tianjin, resulting in high local concentration pollution. Air quality can be affected by convergence, surrounding pollutants gathered in the convergence area located in Tianjin. The air quality in this city reached a serious pollution level, but the air quality in surrounding cities was basically excellent.
What can be done to improve the air quality in Tianjin?
Since its launch in September 2017, the Tianjin tracking research team has carried out a large number of scientific research activities and accumulated various scientific data through comprehensive research methods such as field observation, laboratory analysis and numerical simulation based on the air pollution observation network of space, earth and air. Tens of millions have achieved some preliminary results in the cause of air pollution in Tianjin. In the average PM2.5 contribution during autumn and winter, local primary pollutant emissions account for about 40 per cent, and regional transmission accounts for about 30 per cent. Second, in the past few years, Tianjin’s targeted pollution control measures are the main reason for the obvious improvement in ambient air quality, which also shows that Tianjin’s pollution control methods are correct. Third, the mutual transmission of air pollution between cities exists objectively, but local emissions are the main source of air pollution in Tianjin and most cities.
The development and utilization of clean energy is a long-term strategy for optimizing the energy structure. Improving energy exploitation efficiency and enhancing the coal-fired structure are also important directions for energy structure adjustment. Burning coal will cause pollution, and doing a good job of writing about coal and promoting the clean and efficient use of coal is an important way to lessen pollution caused by coal.
What are the effects on health through breathing in Tianjin’s polluted air?
Not everybody is affected by air pollution in the same way. A strong, young healthy person will be less affected than an older person who already suffers from respiratory problems. It also depends on the levels of concentration of the pollutants, and indeed, the pollutants themselves as well as the length of exposure.
Exposure to high levels of air pollution can cause immediate health problems such as aggravated cardiovascular and respiratory illness, and can actually damage cells permanently.
People with pre-existing health problems should be extra careful as should pregnant women, children under 14 years of age and senior citizens.
Tianjin air quality data attribution
Where is the cleanest air quality in Tianjin?
- North Ring Road 127
- Tuanbo 146
- Zhongshan North Road 149
- Jinyu Road 151
- Binshui East Road 152
- Yong Ming Lu 152
- 4th street 153
- Huaihe Road 153
- Qianjin Road 153
- Yongyang West Road 153
- Dali Road 154
- Xisidao 156
- Da Zhi Gu 8th Rd 157
- De wei Road 157
- Hexi Yijing Road 158
- Qinjian road 158
- Yuejin Lu 158
- Xin Lao Lu 161