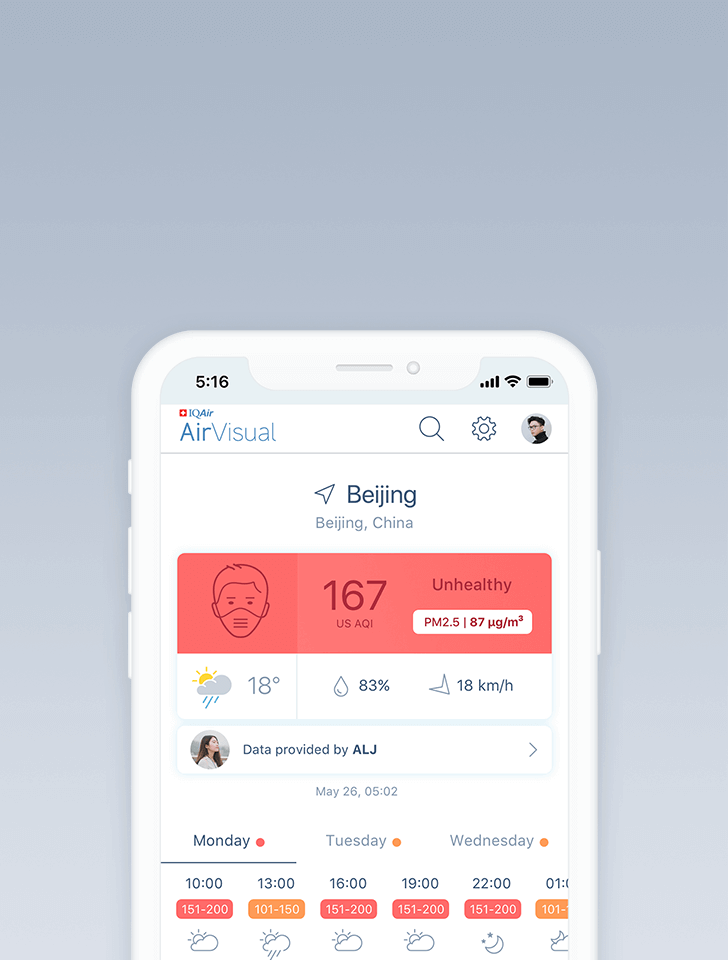
Air quality in Dezhou
Air quality index (AQI) and PM2.5 air pollution in Dezhou
28.5K people follow this city

Dezhou Air Quality Map
Real-time Dezhou air pollution map
Weather
What is the current weather in Dezhou?
| Weather | Clear sky |
| Temperature | 64.4°F |
| Humidity | 14% |
| Wind | 8.5 mp/h |
| Pressure | 30.1 Hg |
live aqi city ranking
Real-time China city ranking
| # | city | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |  Jiayuguan, Gansu Jiayuguan, Gansu | 1273 |
| 2 |  Zhangye, Gansu Zhangye, Gansu | 918 |
| 3 |  Haixi, Qinghai Haixi, Qinghai | 199 |
| 4 |  Jinchang, Gansu Jinchang, Gansu | 180 |
| 5 |  Alxa League, Inner Mongolia Alxa League, Inner Mongolia | 155 |
| 6 |  Guli, Zhejiang Guli, Zhejiang | 151 |
| 7 |  Wuda, Inner Mongolia Wuda, Inner Mongolia | 141 |
| 8 |  Wuxi, Hunan Wuxi, Hunan | 137 |
| 9 |  Yiyang, Hunan Yiyang, Hunan | 134 |
| 10 |  Chengdu, Sichuan Chengdu, Sichuan | 132 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKING3D animated air pollution map
live Dezhou aqi ranking
Real-time Dezhou air quality ranking
| # | station | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gucheng Jackie Chan Middle School | 77 |
| 2 | Gucheng Housing and Urban-rural Development Bureau | 56 |
| 3 | Lingcheng Art Center | 56 |
| 4 | Sun City Middle School | 56 |
| 5 | Jingxian No.1 Middle School | 53 |
| 6 | Supervision station | 49 |
| 7 | ertong leyuan | 49 |
| 8 | Peoples Hospital of Development Zone | 47 |
| 9 | Jiuququanchunjingshuichang | 46 |
| 10 | Wuqiao Sangyuan Town Government | 43 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKINGUS AQI
45
live AQI index
Good
Overview
What is the current air quality in Dezhou?
| Air pollution level | Air quality index | Main pollutant |
|---|---|---|
| Good | 45 US AQI | O3 |
| Pollutants | Concentration | |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 4.5µg/m³ | |
| PM10 | 35µg/m³ | |
| O3 | 109µg/m³ | |
| NO2 | 12µg/m³ | |
| SO2 | 5µg/m³ | |
| CO | 300µg/m³ | |
PM2.5 concentration in Dezhou air currently meets the WHO annual air quality guideline value
Health Recommendations
What is the current air quality in Dezhou?
| Enjoy outdoor activities | |
| Open your windows to bring clean, fresh air indoors GET A MONITOR |
Forecast
Dezhou air quality index (AQI) forecast
| Day | Pollution level | Weather | Temperature | Wind |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunday, May 12 | Moderate 77 AQI US | 82.4° 59° | ||
| Monday, May 13 | Moderate 99 AQI US | 91.4° 59° | ||
| Tuesday, May 14 | Moderate 92 AQI US | 96.8° 68° | ||
| Today | Good 45 AQI US | 77° 60.8° | ||
| Thursday, May 16 | Moderate 100 AQI US | 91.4° 59° | ||
| Friday, May 17 | Unhealthy for sensitive groups 119 AQI US | 98.6° 69.8° | ||
| Saturday, May 18 | Unhealthy for sensitive groups 133 AQI US | 104° 71.6° | ||
| Sunday, May 19 | Unhealthy for sensitive groups 113 AQI US | 98.6° 78.8° | ||
| Monday, May 20 | Unhealthy for sensitive groups 108 AQI US | 87.8° 68° | ||
| Tuesday, May 21 | Unhealthy for sensitive groups 111 AQI US | 93.2° 64.4° |
Interested in hourly forecast? Get the app
How to best protect from air pollution?
AIR QUALITY ANALYSIS AND STATISTICS FOR Dezhou
What is the current level of air pollution in Dezhou?
Dezhou is a prefecture-level city in the north-western province of Shandong in the People's Republic of China. It sits on the banks of the Yellow River and also the Grand Canal runs through the city making it an excellent transportation hub for watercraft. It is also well connected by the rail network with four mainlines running through it. In 2019 it recorded a population of approximately 5.7 million residents.
In the first half of 2021, Dezhou was experiencing a period of “Moderate” air quality with a US AQI reading of 95. This classification is in accordance with recommendations by the World Health Organisation (WHO). It is an internationally recognised system that enables comparisons to be made between different cities in different countries by using the same metrics. Usually, there are six commonly found pollutants in the atmosphere which are measured to form the basis of the system.
The recorded concentrations of these six pollutants were as follows: PM2.5 - 33 µg/m³, PM10 - 133 µg/m³, ozone (O3) - 52 µg/m³, nitrogen dioxide (NO2) - 26 µg/m³, sulphur dioxide (SO2) - 6.5 µg/m³ and carbon monoxide (CO) - 400 µg/m³. The advice for people to follow when pollution levels are this high is to stay indoors as much as possible and to close doors and windows to keep the polluted air outside. Those people who are sensitive to pollution should avoid going outside until the air improves. The table at the top of this page will help you to decide when it is safe to venture outside again. The wearing of a good quality mask is always beneficial.
Does the level of air pollution differ throughout the year in Dezhou?
Air pollution can be very volatile and can change very quickly depending on many variables. It is affected by the changing weather throughout the different seasons of the year. The figures have now been released for 2020 on the IQAir website so it can be seen how it changes.
The best air quality was found during the warmer summer months between April and the end of September when the quality was classed as “Moderate” with figures between 12.1 and 35.4 µg/m³. A slight decline occurred during February and March when the air quality was “Unhealthy for sensitive groups” with readings between 35.5 and 55.4 µg/m³. A similar pattern showed itself in autumn during October and November with respective figures of 48.1 and 51.5 µg/m³. The colder winter months of January and December returned the worst figures of 132.7 and 89.6 µg/m³ which classed the quality as “Unhealthy”.
Records of the air quality in Dezhou were first kept in 2017 when the recorded figure was 68.5 µg/m³. This was followed in 2018 by a marked improvement when the figure was 54.8 µg/m³. A slight decline was noted in 2019 when the figure fell to 53.4 µg/m³ and again in 2021 when the figure dropped again to 50.1 µg/m³. This might be artificially lower because of the restrictions imposed because of the COVID-19 pandemic when the use of personal vehicles was restricted and non-essential industry was also suspended in order to prevent the spread of the virus.
Where does the pollutant PM2.5 come from in Dezhou?
The "contribution" of pollution from motor vehicle exhausts has increased, and agricultural pollution has also added to the atmosphere.
Ongoing studies are still trying to discover exactly what PM2.5 pollutants consist of. Organic matters are ranked first and at present, there are more than 100 types of organic matter under test, mainly from the primary emission of loose coal combustion, motor vehicle exhausts and the secondary conversion of volatile organic compounds. With the effective control of loose coal combustion emissions, the proportion of organic matter is declining.
As one of the main pollutants in the atmosphere, sulphur dioxide is an important factor leading to acid rain, and it was also the most important source of secondary PM2.5. Many regions have always regarded the control of total sulphur dioxide emissions as the top priority of air pollution control.
The major source of nitrogen oxides is road-mobile sources, that is, motor vehicles, accounting for 32 per cent; non-road mobile sources are construction machinery, agricultural machinery, and ships. Emissions from aircraft and other industries accounted for 17 per cent; emissions from the electricity and heating industries accounted for 17 per cent; emissions from other industries accounted for 20 per cent.
One specific source of this pollutant was heavily fined for the pollution it discharged into the atmosphere it was also told to make a public apology for its wrongdoings. The glass producer had emitted hundreds more tonnes of sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxide and smoke dust than the maximums stipulated by regulations.
What does the future hold for industry in Dezhou?
A new industrial zone is currently being built which is affectionately known as “Solar Valley”. Its purpose is for experimenting with clean-energy urban projects and massive use of household utilities such as solar-powered water heaters. Solar energy is one of the largest industry types in Dezhou and one company has developed into being the largest solar-powered water heater manufacturer in the world. It is actively experimenting with photoelectricity.
Dezhou is also home to the largest solar-powered office building which covers a huge 75,000 square metres.
What effect does polluted air have on human health?
Air pollution has many potential health effects, ranging from subtle physiological changes in the body to obvious symptoms such as itchy nose and throat, wheezing, coughing, chest pain or chest tightness.
The most common air pollutants include carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, ozone, suspended particulates, sulphur dioxide and lead.
Carbon monoxide reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of red blood cells, and its impact on health depends on the length of time the body is exposed to it and the concentration of it that is inhaled. Most people experience headaches, dizziness and fatigue when they inhale low levels of carbon monoxide. When inhaling high concentrations, it can cause blurred vision, loss of coordination, and even death.
Nitrogen dioxide can irritate the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose, throat and respiratory tract. Exposure to low concentrations can cause bronchial allergies and aggravate asthma patients' reactions to allergens. In addition, it will also worsen the condition of patients with chronic respiratory diseases. Prolonged exposure to it may weaken lung function and reduce the ability of the respiratory system to fight diseases.
Dezhou air quality data attribution
Where is the cleanest air quality in Dezhou?
- Jingxian Market Supervision Bureau 42
- Wuqiao Sangyuan Town Government 43
- Jiuququanchunjingshuichang 46
- Peoples Hospital of Development Zone 47
- Supervision station 49
- ertong leyuan 49
- Jingxian No.1 Middle School 53
- Gucheng Housing and Urban-rural Development Bureau 56
- Lingcheng Art Center 56
- Sun City Middle School 56
- Gucheng Jackie Chan Middle School 77