Get a monitor and contributor to air quality data in your city.
21.2K people follow this city





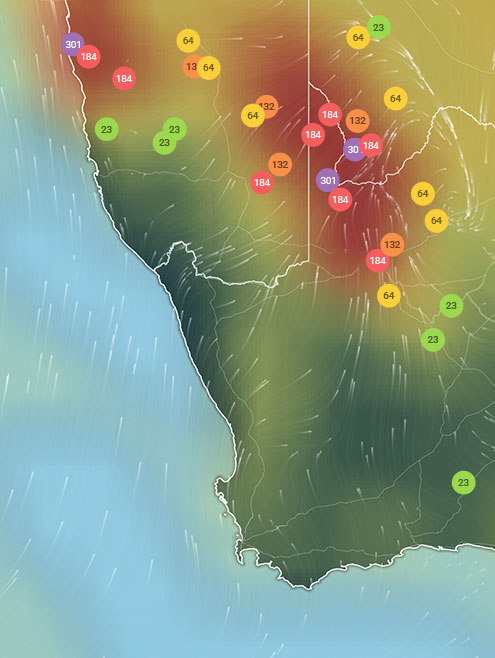
AIR QUALITY DATA CONTRIBUTORS
Find out more about contributors and data sources| Index | None | ||
| Tree pollen | None | ||
| Grass pollen | None | ||
| Weed pollen | None |
| Weather | Rain |
| Temperature | 87.8°F |
| Humidity | 65% |
| Wind | 8.1 mp/h |
| Pressure | 29.8 Hg |
| # | city | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |  Corpus Christi, Texas Corpus Christi, Texas | 85 |
| 2 |  Flagstaff, Arizona Flagstaff, Arizona | 77 |
| 3 |  La Habra, California La Habra, California | 75 |
| 4 |  Thibodaux, Louisiana Thibodaux, Louisiana | 75 |
| 5 |  Anaheim, California Anaheim, California | 68 |
| 6 |  Galveston, Texas Galveston, Texas | 68 |
| 7 |  La Mirada, California La Mirada, California | 67 |
| 8 |  Monrovia, California Monrovia, California | 66 |
| 9 |  Yorba Linda, California Yorba Linda, California | 66 |
| 10 |  Chino Hills, California Chino Hills, California | 65 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKING
| # | station | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Model City | 34 |
| 2 | Coconut Grove | 28 |
| 3 | Southwest 88th Lane | 27 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKINGUS AQI
28
live AQI index
Good
| Air pollution level | Air quality index | Main pollutant |
|---|---|---|
| Good | 28 US AQI | PM2.5 |
| Pollutants | Concentration | |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 5.1µg/m³ | |
PM2.5 concentration in Miami air currently meets the WHO annual air quality guideline value
| Enjoy outdoor activities | |
| Open your windows to bring clean, fresh air indoors GET A MONITOR |
| Day | Pollution level | Weather | Temperature | Wind |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuesday, May 7 | Good 34 AQI US | 82.4° 77° | ||
| Wednesday, May 8 | Good 31 AQI US | 82.4° 78.8° | ||
| Thursday, May 9 | Good 26 AQI US | 89.6° 78.8° | ||
| Today | Good 28 AQI US | 89.6° 78.8° | ||
| Saturday, May 11 | Good 49 AQI US | 93.2° 77° | ||
| Sunday, May 12 | Moderate 52 AQI US | 84.2° 78.8° | ||
| Monday, May 13 | Moderate 54 AQI US | 82.4° 78.8° | ||
| Tuesday, May 14 | Moderate 56 AQI US | 84.2° 80.6° | ||
| Wednesday, May 15 | Moderate 69 AQI US | 91.4° 80.6° | ||
| Thursday, May 16 | Moderate 60 AQI US | 87.8° 78.8° | ||
| Friday, May 17 | Moderate 59 AQI US | 84.2° 80.6° |
Interested in hourly forecast? Get the app
Miami, the southeastern Florida metropolis, experiences elevated air pollution levels common to urban areas. Miami-Dade County ranks as the most populous county in Florida and the seventh most populous county in the United States, with 2.7 million residents and another 4.2 million residents in the surrounding area.1 Air pollution emissions result from transportation congestion, domestic energy consumption, regional port activity, industry, power generation, and natural sources, including wind-blown salt and sand.
Despite its large urban population, Miami air quality fares better than most comparably sized cities as a result of its coastal peninsula geography. With the Atlantic Ocean to the east and Gulf Coast to the west, the southern tip of Florida is surrounded by bodies of water that greatly reduce the influence of transboundary air pollution and provide ideal conditions for local emissions to readily disperse. This geographical feature is largely to thank for Miami’s generally “good” air quality, as defined by the US EPA Air Quality Index (AQI).
According to data collected by the American Lung Association State of the Air (SOTA) report, Miami met US EPA-based standards for daily ozone, daily PM2.5, and annual PM2.5 in the 2017-2020 monitoring period.2 Miami has also succeeded in passing federal air quality standards since 2009, the first year ozone fell within compliance levels, and met annual or daily PM2.5 standards since records began in 2000.
Despite compliance with federal standards, no level of air pollution exposure is completely safe.3 Moreover, air pollution in Miami still reaches levels deemed “unhealthy for sensitive groups” and higher. It is important to check Miami’s real-time AQI levels and Miami’s forecast air quality conditions to understand the level of risk present in the air and the actions one can take to reduce exposure.
Miami air quality is relatively consistent year-round due to its tropical climate. Temperatures typically vary from 62°F to 90°F and are rarely recorded outside this range.4 Generally warm temperatures also means that there is relatively little change in human behavior throughout the year – winter woodburning and car idling (for heating purposes) remain rare.
In 2020, average monthly PM2.5 concentrations ranged from a low of 5.4 μg/m3 in November to a high of 9.9 μg/m3 in July. Every month of the year met the US PM2.5 target of 12 μg/m3 as well as the more stringent World Health Organization (WHO) PM2.5 target of 10 μg/m3.
Miami does observe subtle seasonal variation, however, in monthly PM2.5 levels. The winter months are prone to heavy rains, which coagulate and tamp down air pollutants. In 2020, the months of November and December averaged exceptionally low PM2.5 concentrations of 5.4 μg/m3 and 4.9 μg/m3 (respectively).
While Miami is a large urban metropolis and popular cruise port, the city fares relatively well for air quality. Miami ranks as the 28th most polluted city in Florida (out of 48 cities) and the 996th most polluted city in the United States (out of 1,412 cities).
In 2020, Miami averaged an annual PM2.5 concentration of 7.9 µg/m³. By comparison, the 5 most polluted cities in Florida during 2020 averaged concentration levels several micrograms higher:
Miami is the “cruise capital of the world”, a designation that carries a heavy air pollution burden. A study by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) found that a single docked cruise ship contributes as much diesel exhaust as 34,400 idling heavy-duty semi-trucks.5 In the Port of Miami, nine cruise ships are typically docked at a time, producing air pollution equivalent to that of roughly 310,000 trucks.
In 2021, the Port of Miami won a $2 million dollar grant from the U.S. EPA aimed at slashing diesel exhaust from cruise ships.6 The grant money will fund plugs into the local electrical grid so that ships can run on electricity at the port rather than idling their engines. This investment (combined with $8 million in funding from the city of Miami) could reduce the prevalence of harmful gas pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide emissions, by 67 percent and 99 percent (respectively) while also cutting emissions of carbon, a potent greenhouse gas, by up to 35 percent.
Transportation emissions, primarily from motor vehicles and highway congestion, are also major sources of Miami air pollution that the city seeks to address. It is estimated that shifting to 100-percent electric vehicle usage within the city limits could help clear Miami’s polluted sky, avoiding 126 premature deaths annually and $1.4 billion USD in public health costs.7 Currently, there is little in the way of incentives and tax rebates from the city of Miami for residents choosing electric vehicles (EVs). At the start of 2021, however, Florida’s Energy Office released its first electric vehicle roadmap aimed at accommodating EV growth, which officials hope is quickly adopted and implemented.8 While progress is seemingly underway, more must be done to ease and promote the transition to electric vehicles.
While Miami air quality meets the U.S. EPA’s most stringent air pollution standards for PM2.5 and ozone, no level of air pollution has proven to be free of health consequences.
A 2019 study published in PLoS Medicine found that air pollution levels that meet current EPA standards still contribute to unnecessary deaths and adverse health effects.9 Further lowering the PM2.5 standard below 12 μg/m3 could provide an opportunity to improve the health and livelihood of residents as well as equalize the health burden across income levels (as under-resourced neighborhoods are often exposed to higher particle pollution levels).
Exposure to PM2.5 pollution can aggravate cardiovascular and respiratory illnesses such as asthma, bronchitis, emphysema, COPD, and congestive heart failure as well as cause cancer and contribute to early death. The risk of developing health risks associated with PM2.5 increases with exposure, and is more likely to impact children, the elderly, and those with pre-existing health conditions.
There are a number of means for reducing one’s health risk to air pollution. These include wearing an air pollution mask when Miami’s AQI is above 100, avoiding outdoor activity (especially strenuous activity) during peak pollution periods and using air purifiers where available.
+ Article Resources
[1] United States Census Bureau. (2020). Miami-Dade County, Florida. U.S. Department of Commerce.
[2] American Lung Association. (2020). State of the air – 2020.
[3] World Health Organization. (2020). Air quality guidelines – global update 2005.
[4] Weather Spark. (2021). Average Weather in Miami.
[5] Zimmerman K, et al. (2011). How do cruise emissions and truck emissions stack up? Coastal Conservation League.
[6] Dolven T, et al. (2021, May 8). PortMiami wins $2M EPA grant, one step closer to reducing air pollution from cruise ships. Miami Herald.
[7] Brasileiro A. (2020, September 16). Miami has air quality problems. Study points to electric cars as a healthier option. Miami Herald.
[8] Banahan G. (2021, February 9). Florida’s electric vehicle market is geared for exponential growth but awaiting takeoff. NPR - WUFT.
[9] Bennett J, et al. (2019). Particulate matter air pollution and national and county life expectancy loss in the USA: A spatiotemporal analysis. PLoS Medicine. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002856
3Contributors
3 Anonymous Contributors

3 stations
1 Data source