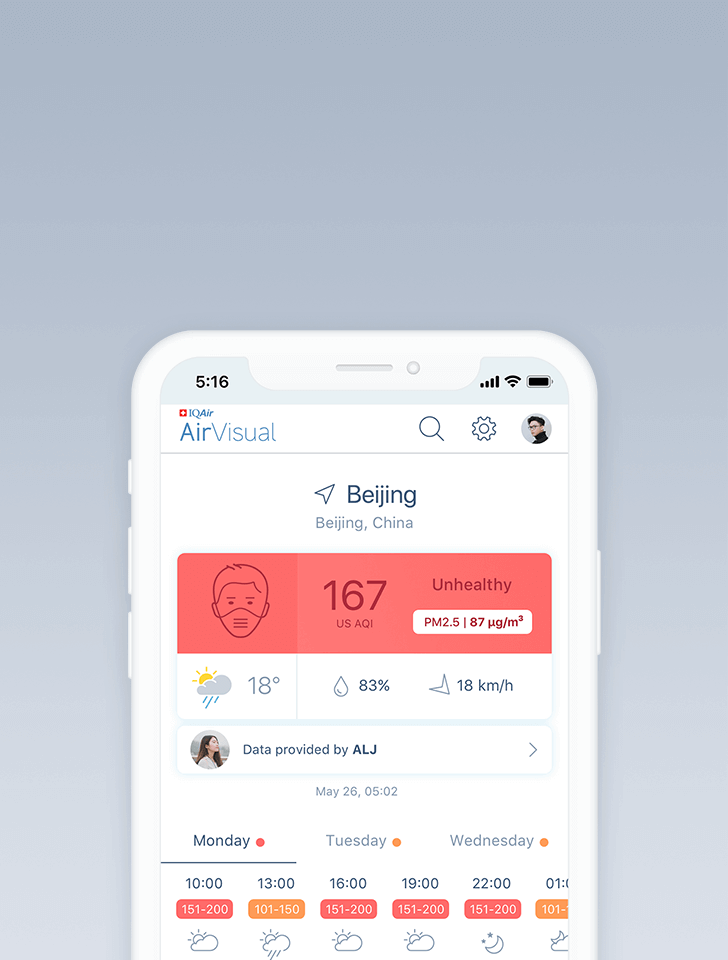
Air quality in Hangzhou
Air quality index (AQI) and PM2.5 air pollution in Hangzhou
317.1K people follow this city
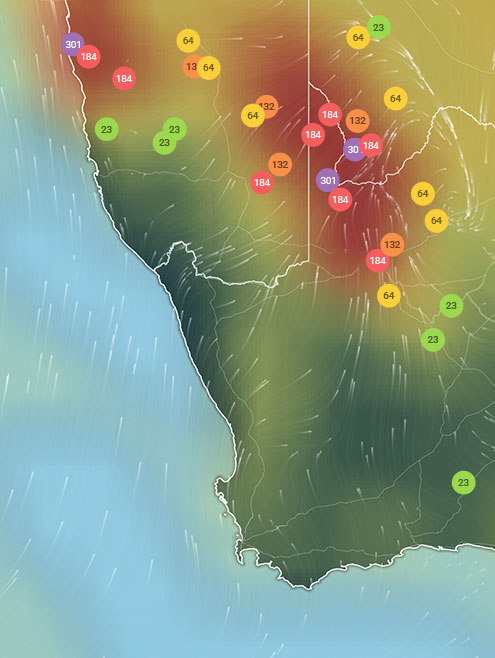
Hangzhou Air Quality Map
Real-time Hangzhou air pollution map
Weather
What is the current weather in Hangzhou?
| Weather | Broken clouds |
| Temperature | 66.2°F |
| Humidity | 86% |
| Wind | 5 mp/h |
| Pressure | 29.9 Hg |
live aqi city ranking
Real-time China city ranking
| # | city | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jinchang, Gansu | 1912 |
| 2 | Datong, Shanxi | 317 |
| 3 | Zhangjiakou, Hebei | 187 |
| 4 | Tieling, Liaoning | 177 |
| 5 | Baoding Shi, Hebei | 173 |
| 6 | Yangliuqing, Tianjin | 173 |
| 7 | Dingzhou, Hebei | 167 |
| 8 | Leshan, Sichuan | 165 |
| 9 | Beijing, Beijing | 164 |
| 10 | Hohhot, Inner Mongolia | 164 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKING3D animated air pollution map
live Hangzhou aqi ranking
Real-time Hangzhou air quality ranking
| # | station | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Linping Town | 132 |
| 2 | Beishan Road | 102 |
| 3 | Wolong Bridge | 88 |
| 4 | Xiaohe Mountain | 80 |
| 5 | Binjiang | 76 |
| 6 | Chengxiang Town | 76 |
| 7 | Fire Brigade | 74 |
| 8 | Yunqi | 74 |
| 9 | Xixi | 72 |
| 10 | Zhejiang Agricultural University | 72 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKINGUS AQI
76
live AQI index
Moderate
Overview
What is the current air quality in Hangzhou?
| Air pollution level | Air quality index | Main pollutant |
|---|---|---|
| Moderate | 76 US AQI | PM2.5 |
| Pollutants | Concentration | |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 24µg/m³ | |
| PM10 | 39µg/m³ | |
| O3 | 67.5µg/m³ | |
| NO2 | 18µg/m³ | |
| SO2 | 4µg/m³ | |
| CO | 550µg/m³ | |
PM2.5
x4.8
PM2.5 concentration in Hangzhou is currently 4.8 times the WHO annual air quality guideline value
Health Recommendations
What is the current air quality in Hangzhou?
| Sensitive groups should reduce outdoor exercise | |
| Close your windows to avoid dirty outdoor air GET A MONITOR | |
| Sensitive groups should wear a mask outdoors GET A MASK | |
| Sensitive groups should run an air purifier GET AN AIR PURIFIER |
Forecast
Hangzhou air quality index (AQI) forecast
| Day | Pollution level | Weather | Temperature | Wind |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wednesday, Apr 24 | Moderate 64 AQI US | 75.2° 59° | ||
| Thursday, Apr 25 | Moderate 84 AQI US | 71.6° 60.8° | ||
| Friday, Apr 26 | Moderate 97 AQI US | 73.4° 60.8° | ||
| Today | Moderate 76 AQI US | 71.6° 60.8° | ||
| Sunday, Apr 28 | Moderate 85 AQI US | 75.2° 62.6° | ||
| Monday, Apr 29 | Moderate 81 AQI US | 80.6° 64.4° | ||
| Tuesday, Apr 30 | Moderate 95 AQI US | 66.2° 55.4° | ||
| Wednesday, May 1 | Moderate 68 AQI US | 60.8° 53.6° | ||
| Thursday, May 2 | Moderate 62 AQI US | 64.4° 53.6° | ||
| Friday, May 3 | Moderate 77 AQI US | 66.2° 57.2° |
Interested in hourly forecast? Get the app
AIR QUALITY ANALYSIS AND STATISTICS FOR Hangzhou
Is Hangzhou a city with bad air quality?
Hangzhou is a city located in the upper northeastern region of China, part of Zhejiang province, located at the southern side of the grand canal of China. It has a long history going back many millennia with a rich cultural heritage, and nowadays finds itself as one of the more desirable cities to live in throughout the country, with large amounts of commercial activity occurring, as well as being a hub for prestigious universities and IT firms.
In regards to its air quality, Hangzhou came in with a PM2.5 reading of 37.4 μg/m³ over 2019, as its yearly average. This reading put Hangzhou into the ‘unhealthy for sensitive groups’ ratings bracket, which requires a PM2.5 reading of anywhere between 35.5 to 55.4 μg/m³ to be classified as such. As the name indicates, those with a sensitivity towards pollution will find themselves at risk, as well as other vulnerable demographics such as young children, the elderly, pregnant mothers and those who are ill or have preexisting conditions being in danger of suffering from adverse effects.
Hangzhou’s PM2.5 reading of 37.4 μg/m³ also placed it in 161st place out of all cities ranked in China, as well as being ranked in 272nd place out of all cities worldwide. This is indicative that whilst Hangzhou does not share the same catastrophic levels of pollution as some of its fellow cities (such as Hotan coming in with a PM2.5 average of 110.1 μg/m³ over 2019), it stands to reason that the air quality is most certainly detrimental to those that breath it year round, particularly during months that see higher levels of smoke, haze and smog permeating the air.
What causes pollution in Hangzhou?
With a population of some 10.36 million inhabitants, Hangzhou will inevitably be subject to rising pollution levels caused by having such a large population, as with the mass movement of people in their daily commutes often comes large amounts of pollution.
One of the main causes would be that of vehicular emissions, with large amounts of urban infrastructure having been built to facilitate the ease of vehicle usage, causing many personal vehicles to be relied upon by the its citizens, although in recent years initiatives to reduce this with the use of more public transport as well as public bikes being put into play to reduce the effects of vehicular fumes and emissions.
Other sources of pollution would be from factories and industrial areas, many of which run on fossil fuels such as coal, giving off heavy amounts of pollution emanating from the combustion of this coal, as well as whatever industrial effluence is released as a byproduct of the materials or goods being produced.
So, to finish, with a rise in private car ownership as well as lower quality fuel being used (that also happens to be heavily subsidized and therefore finds it usage more prevalent), the main cause of pollution in Hangzhou comes from vehicles, with factories and other similar areas such as construction sites also contributing to the ambient year round pollution levels.
When is the air quality at its worst in Hangzhou?
Observing the data taken over the course of 2019, the months that stand out as having higher levels of PM2.5 were at the end of the year and very beginning of the year, with the months of October to December as well as January through to April all having the highest PM2.5 readings.
PM2.5 refers to fine particulate matter that is 2.5 micrometers or less in diameter, making it approximately 3% the size of a human hair and thus extremely dangerous to respire. It is due to this reason that it is used as a major component in calculating the quality of the air and how safe it is to breath.
Regarding the most polluted months, January came in with the highest PM2.5 reading at 62.9 μg/m³, putting it into the ‘unhealthy’ ratings bracket (55.5 to 150.4 μg/m³ required for classification), with December, February and March all following closely behind with similar readings, indicating that the colder months of the year are when pollution levels will be at their absolute worst.
When is the air quality cleanest in Hangzhou?
Contrasting the previous question, the air quality levels are shown to be at their best during the summer months in Hangzhou. The reasons behind this may be due to a decrease in the amount of heating being used in houses and places of business, which in turn leads to a large increase in the amount of energy being expended, typically finding its source from fossil fuel based factories. To a lesser extent, people in low income districts as well as provincial areas may resort to burning coal or other organic materials such as wood to provide heat for their homes, as well as for cooking, although this has largely been phased out in recent times and does not contribute as much to the overall pollution levels.
Looking once again at the data, the cleanest months ran from May through to September, with all of those months falling into the ‘moderate’ pollution bracket, a rating which requires a PM2.5 reading of anywhere between 12.1 to 35.4 μg/m³ to be classified as such.
The month with the lowest levels of PM2.5 was July, which came in with a PM2.5 reading of 20.8 μg/m³, followed closely by August and September, before the pollution levels began to rise rapidly again.
What are some health risks associated with pollution in Hangzhou?
With Hangzhou seeing PM2.5 readings go as high as 62.9 μg/m³ in January of 2019, it is evident that there would be some highly negative health risks that come along with this, although of note is that any reading above the WHO’s target number of 10 μg/m³ or less can present health issues, particularly to vulnerable demographics or those caught in highly polluted areas (such as those that have to take daily commutes in heavy traffic).
Health problems would include ailments such as increased rates of lung cancer, as well as respiratory illnesses such as bronchitis, pneumonia, emphysema and asthma, with vehicle pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide (NO2) being notorious for triggering off aggravated forms of asthma attacks and worsening other respiratory conditions.
Fine particulate matter can make its way into the blood stream via the lungs, and cause large amounts of damage to the blood vessels, the heart, the liver and kidneys as well as affecting the reproductive system, causing a reduction in fertility rates. These are but a few of the health conditions associated with breathing polluted air in Hangzhou.